Welcome! In the world of web development, two core roles make up every digital experience: Frontend and Backend. While one focuses on what you see, the other manages the unseen data and logic. Today, we'll dive deep into both to define their core technologies, responsibilities, and how they work together to build a functional website. By the end of this post, you'll have a clear understanding of the difference between client-side and server-side development. Let's get started!
Frontend
Frontend refers to the "client-side" of a website, or everything a user sees and interacts with directly in their web browser. It is primarily focused on creating the user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) to ensure a website is visually appealing, easy to navigate, and highly responsive.
Core technologies
Frontend development is built on three main programming languages:
- HTML (HyperText Markup Language): The foundation that structures the content of a web page, such as headings, paragraphs, and links.
- CSS (Cascading Style Sheets): Used to style the visual presentation of a website, controlling the colors, fonts, layout, and animations.
- JavaScript: A programming language that adds dynamic functionality and interactive elements to a website, such as drop-down menus, image carousels, and form validation.
Key responsibilities of a frontend developer
The day-to-day work of a frontend developer involves a variety of tasks:
- Creating the user interface: Building layouts and user interfaces that are both functional and enjoyable for the user.
- Ensuring responsiveness: Using techniques like responsive web design to ensure the website looks and works correctly on all devices, from desktop computers to mobile phones.
- Optimizing performance: Improving a website's speed and efficiency by minimizing load times and reducing the overall size of assets like images and scripts.
- Testing and debugging: Ensuring the website performs as intended and fixing any errors that users might encounter.
- Collaborating with other teams: Working with backend developers, UI/UX designers, and project managers to bring a product from concept to a polished, functional website.
The Partnership with UI/UX Design
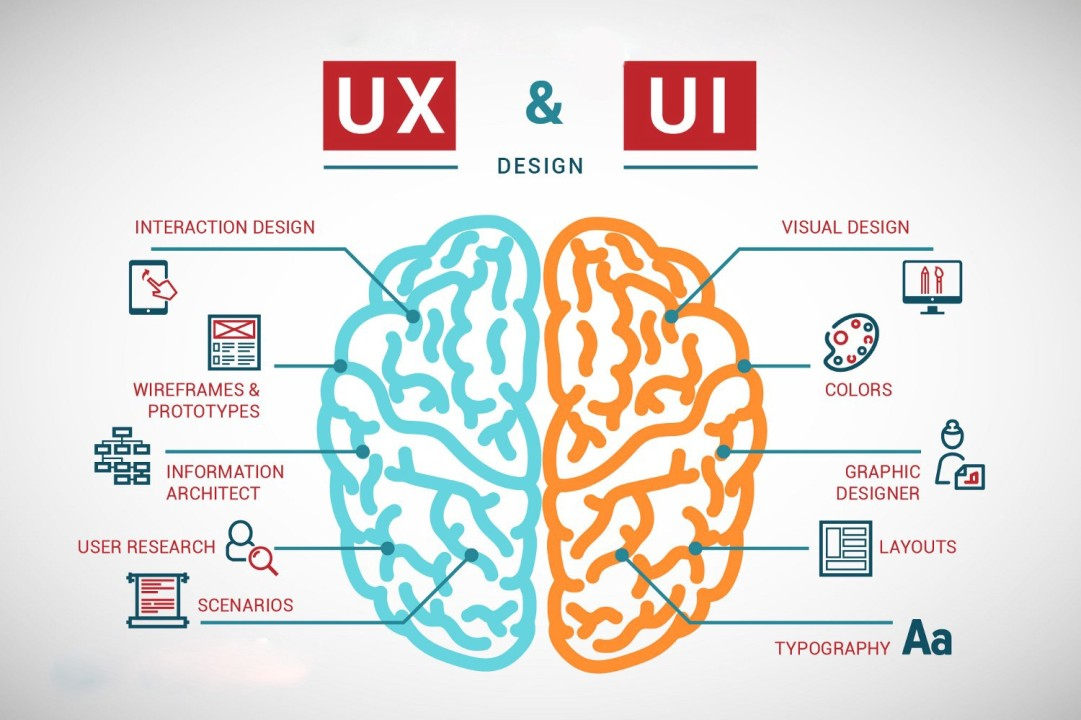
The visual appeal and user-friendliness of a website, which are the main focus of frontend development, originate with UI/UX Designers.
- UI (User Interface) Design focuses on the aesthetics of the website — what the user sees, such as colors, typography, buttons, and layout.
- UX (User Experience) Design focuses on how the user interacts with the site — ensuring the website is easy, efficient, and enjoyable to navigate.
The frontend developer's primary role is to take the polished visual and interactive blueprints created by the UI/UX designers and translate them into functional, production-ready code using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. This means a frontend developer often collaborates closely with UI/UX designers to bring a product from concept to a polished, functional website.
Backend
Backend development, or "server-side" development, refers to the programming that happens behind the scenes to manage and support a web application. It is the unseen foundation that handles logic, data management, and communication between the browser (frontend) and the server.
Core functions and responsibilities
Backend developers focus on the inner workings of an application to ensure it runs efficiently and reliably. Their key functions include:
- Database management: Designing, creating, and managing databases to store and retrieve data. This can include optimizing queries to ensure data is accessed quickly and reliably.
- Application logic: Writing the core business logic that dictates how the application functions. For example, processing a user login, calculating shipping costs for an online order, or searching a product catalog.
- API development: Building Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) that enable the frontend to communicate with the backend. The API acts as a middle layer, sending user requests to the server and returning the appropriate data.
- Server management: Handling the server environment where the application is hosted. This can involve configuring the server, managing resources, and ensuring it can handle many user requests simultaneously.
- Security: Implementing security measures to protect sensitive data. This includes handling authentication, encryption, and protection against common attacks like SQL injection.
Common technologies
Backend developers work with a diverse set of technologies, often based on the specific project requirements.
- Languages: Popular server-side languages include:
- Python (often with frameworks like Django or Flask)
- JavaScript (using the Node.js runtime)
- Java (with frameworks like Spring Boot)
- PHP (with frameworks like Laravel or Symfony)
- Ruby (with the Ruby on Rails framework)
- Databases: To manage data, developers use both SQL and NoSQL databases:
- SQL (relational): MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle
- NoSQL (non-relational): MongoDB and Cassandra
- Servers: Applications are hosted on web servers, with common choices including Apache and Nginx.
- Cloud platforms: For hosting and managed services, developers often use cloud platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud Platform (GCP), or Microsoft Azure.
Frontend VS Backend
| Feature | Frontend | Backend |
|---|---|---|
| Common Name | Client-side Development | Server-side Development |
| Focus | What users see and interact with directly in the browser | The invisible infrastructure that provides and processes data |
| Primary Goal | Creating the User Interface (UI) and User Experience (UX) to ensure visual appeal, navigability, and responsiveness | Handling logic, data management, and communication between the browser and the server |
| Core Technologies |
|
|
| Key Responsibilities |
|
|
The Full Stack Developer
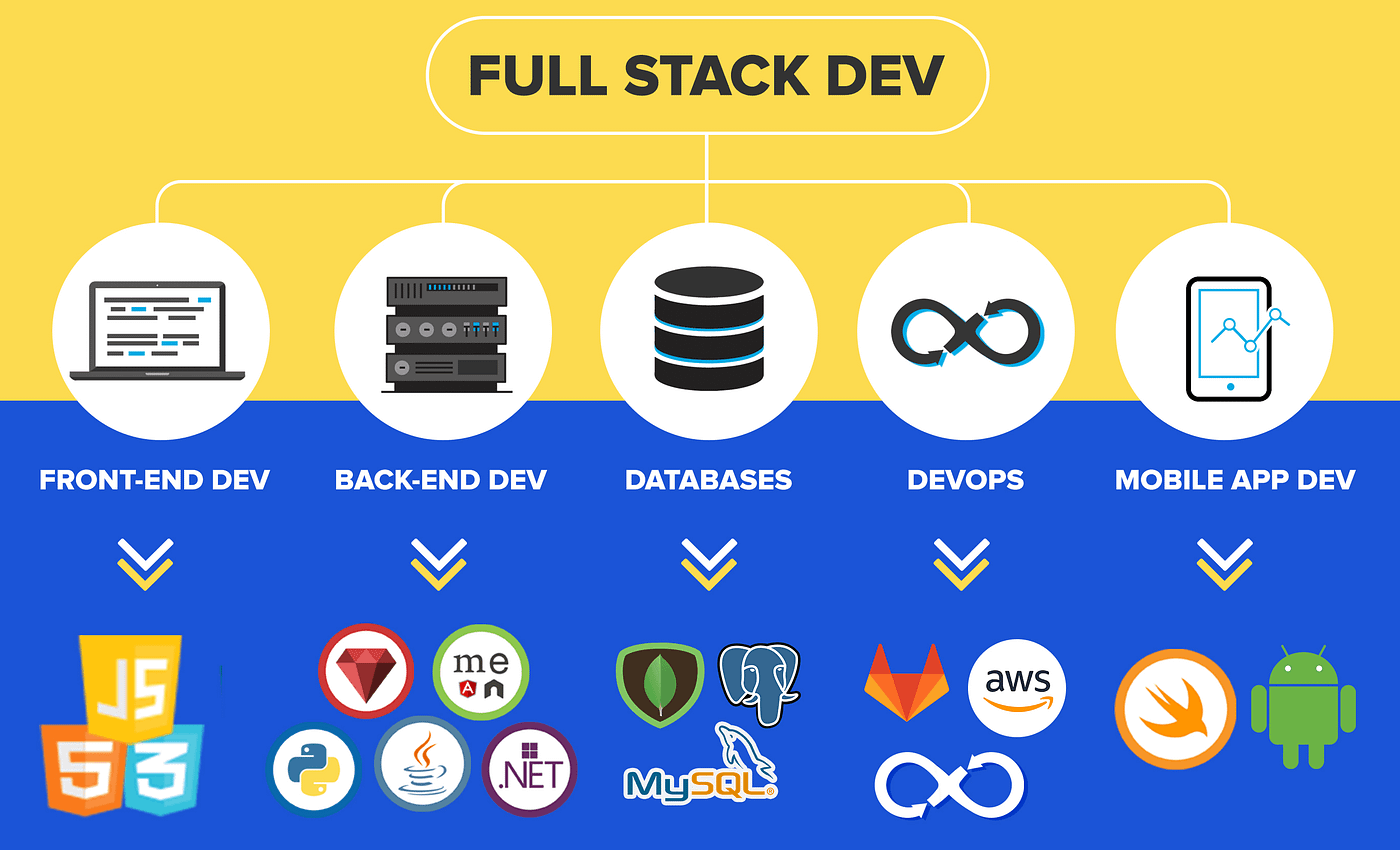
While frontend and backend development are distinct specializations, a Full Stack Developer is proficient in working across both. A full-stack developer has the skills to handle all layers of a web application — from the visual user interface (frontend) to the server logic and database management (backend). This role requires a comprehensive understanding of both client-side and server-side operations, making full-stack developers versatile and highly valued. This breadth of knowledge allows them to:
- Understand and manage the entire web application process from concept to deployment.
- Bridge the communication gap between dedicated frontend and backend teams.
- Make design and architectural decisions that benefit both sides of the application.
Commonly, a full-stack developer will specialize in a specific stack of technologies, such as the MERN stack (MongoDB, Express.js, React, Node.js) or the LAMP stack (Linux, Apache, MySQL, PHP).
Conclusion
In summary, the web is built on a fundamental partnership: the Frontend and the Backend.
The frontend is the canvas, using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to translate visual designs from UI/UX specialists into the interactive, responsive experience you see in your browser. Conversely, the backend is the hidden engine, providing security, managing data in databases, and writing the core application logic that makes the site functional and reliable.
Understanding these distinct but interconnected domains is key to appreciating how modern web applications function. Whether a developer specializes in one area or masters both as a Full Stack Developer, the ultimate goal is the same: to deliver a seamless, efficient, and secure digital experience.
Thank you for reading and have a wonderful rest of your day.👋